It’s no secret that collagen in skin care is the key to a youthful-looking complexion. This structural protein provides much-needed support and stability to keep the skin firm, plump and springy. Unfortunately, the body's store of collagen rapidly declines as we age. Read on to learn about what collagen does for the skin, the different types of collagen, plus the benefits of collagen and how it can keep skin looking ageless.
What Is Collagen?
Collagen is a smaller form of protein that helps to build our tissues and organs, including our bones, muscles, skin and even teeth. This structural protein gets its name from the Greek word “kolla," meaning glue (a helpful hint about the role it plays in the body). Collagen is what binds our cells and tissues together, helping them retain their shape, elasticity and strength.
The majority of collagen is found and produced in the dermis (the skin’s second layer). Here, fibroblasts synthesize strands of collagen which look like long braids or ropes. According to SELF: “Individual amino acids link up to form long chains, which bundle together to form thicker strands. Those strands then twist and coil around each other to form triple helices. Finally, those helices connect end to end and stack on top of each other to form clusters called fibrils.” These fibrils form a collagen network that gives the skin its underlying structure and support.
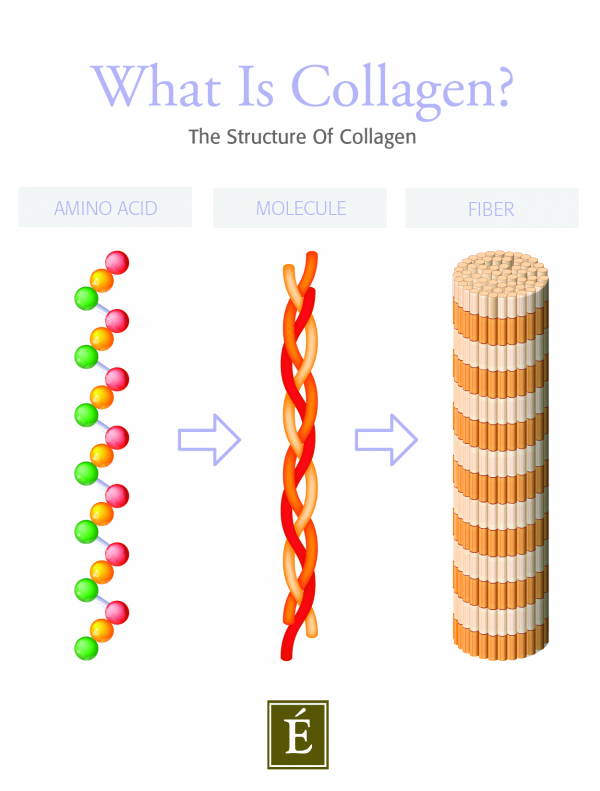
3 Types of Collagen
There are 28 types of collagen found in the body, but Type I, II and III are the most plentiful. These three types constitute up to 90 percent of the body’s total collagen supply. Here’s a breakdown of how they differ:
Collagen Type I
Type I is the most common type of collagen and provides structural support for our bones, organs and connective tissues (including the skin). It is incredibly elastic and can stretch considerably without breaking. In fact, an MIT study found that Type I collagen fibrils are five to ten times stronger than steel.
Collagen Type II
Type II collagen is the building block of cartilage. Unlike Type I collagen which is neatly arranged, Type II forms more of a jumble. This arrangement gives cartilage its flexible, springy quality which allows it to easily compress and cushion our joints.
Collagen Type III
Type III collagen is most concentrated in bone marrow and lymph tissues. Its narrow fibers are arranged in branches that provide support for specialized cells involved in blood cell generation. It is often found alongside Type I collagen in the skin and plays a key role in wound repair.
What Does Collagen Do for Skin?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the skin, and for good reason. This structural protein provides strength, support and elasticity to keep the skin firm, plump and youthful. Here’s a closer look at how collagen benefits the skin.
Provides Support & Structure
Collagen fibers bind tissue together. With their strong, braid-like composition, they function much like sturdy columns that hold up and support the top layer of skin. When you’re young, these columns provide the stability and rigidity that keep your skin tightened and lifted. This strong foundation keeps your skin’s youthful shape intact. Sagging skin is a natural part of the aging process as skin loses elasticity and collagen production.
Watch this In The Mix video to learn what products to use to help lift, tighten and firm sagging skin.
Keeps Skin Firm & Plump
Along with elastin and hyaluronic acid, collagen is found in the dermis, the middle layer of skin that gives it volume, density and bounce. Together, these materials form a tight, flexible collagen network that keeps skin firm, plump and supple. When plentiful, collagen keeps the skin from sagging and prevents the folding and creasing that contributes to fine lines and wrinkles.
Improves Elasticity
That spring and bounce you see in youthful skin? Credit that to collagen. In addition to keeping your complexion firm and plump, collagen improves the skin’s flexibility and elasticity. This not only helps prevent the formation of wrinkles, it also reduces the appearance of stretch marks and cellulite.
Why Do We Lose Collagen?
The skin contains an abundance of collagen when we’re young, but with age it starts to decline. Dr. Hooman Khorasani, a triple board-certified, fellowship-trained cosmetic and skin cancer surgeon based in New York, tells us: “Our skin has a fine balance between collagen production and collagen breakdown. It can take up to six months for collagen to get synthesized in our body. As we get older, corticosteroids tend to halt the production of new collagen and accelerate the breakdown of new collagen.” Exposure to environmental stressors accelerates this process even further. Unhealthy lifestyle habits (like smoking and high sugar intake) as well as stress, pollution and blue-light UV rays cause free radical damage that speeds up collagen depletion. By the time we hit our twenties, we lose roughly one percent of collagen every year.
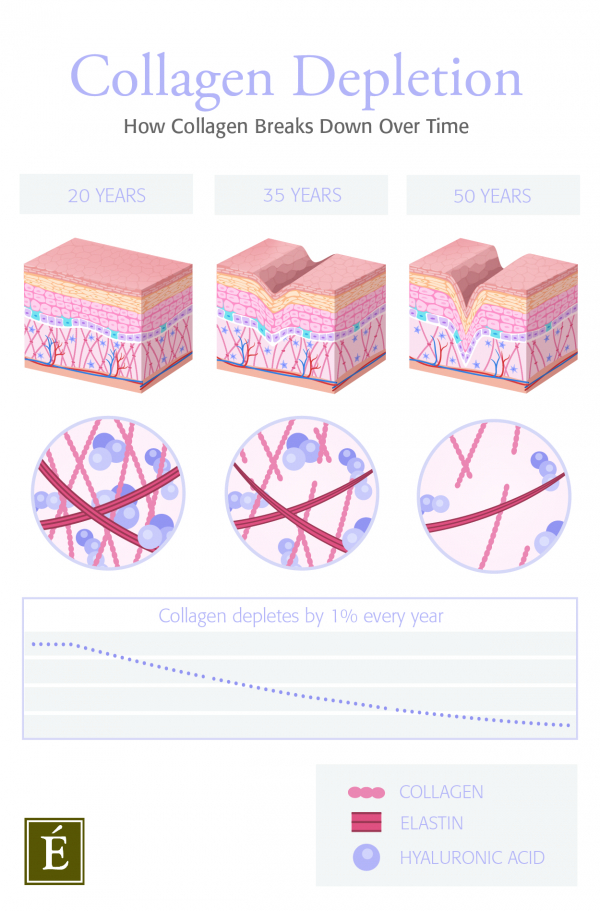
The Result: Visible Signs Of Aging
When we lose more collagen than we produce, the visible signs of aging quickly start to emerge. Weakened collagen cannot provide much-needed structural support and as collagen levels drop, our skin becomes thinner, starts to droop and develops fine lines and wrinkles.
As SHAPE explains, “When collagen is strong, your skin bounces right back. But if collagen is weak, repeated movements cause permanent creases. Skin doesn’t have enough collagen to fill in the groove, so you see a line even when you’re not squinting or furrowing, and it no longer has the same density to resist gravity.”
Ingredients That Stimulate Collagen Production
With collagen’s numerous benefits for the skin, it’s no wonder it’s a hyped ingredient that has begun to pop up in skin care. However, collagen in skin care isn’t quite as simple as tacking it on to an ingredient list. Read on to learn why.
The Problem With Size
The biggest (pun intended) problem with collagen is its size. Dr. Joshua Zeichner tells The Zoe Report: “Pure collagen molecules are too large to actually be absorbed by the body as-is.” Due to their size, these beneficial proteins can’t penetrate the skin. Instead, skin care experts recommend using topical treatments that include ingredients like peptides, retinol and vitamin C which stimulate and protect your skin’s natural collagen production.
Peptides
To bypass the sizing issue, many topical treatments contain collagen peptides. These smaller chains of amino acids are more easily absorbed by the skin because they can pass through the outer layer of the skin. When they reach the dermis, peptides provide the skin’s fibroblasts with the building blocks they need to produce new collagen. By applying peptides through skin care products, we can actually trick the skin into making more of this essential protein.
Retinol
Retinol is another topical ingredient that stimulates collagen synthesis in the skin. According to SHAPE, “Both retinoic acid and retinol ‘turn on’ genes and cells involved in collagen production. They also help organize new and existing collagen.”
Vitamin C
Antioxidants like vitamin C pull double duty and stimulate collagen production as well as protect it from depleting in the future. Vitamin C not only activates the skin’s fibroblasts to produce new collagen, it also stabilizes the collagen you already have, helping skin stay firm, plump and youthful-looking for longer. Look for peptide serums that pair well with antioxidants with vitamin E and ferulic acid. Research shows that these nutrients amplify vitamin C’s effectiveness eight-fold!
Are you ready to explore the benefits of collagen skin care in products like the Marine Flower Peptide Collection? Read more about peptide skin care products and schedule a consultation with a licensed esthetician at an Eminence Organics Spa Partner near you.


.jpg)
