Call them age spots, liver spots, black spots or sun spots. No matter what name they go by, these patches are often signs of skin damage. Here’s what you need to know about dark spots and what’s going on with your skin when hyperpigmentation occurs, why it happens and what skin care solutions to consider.
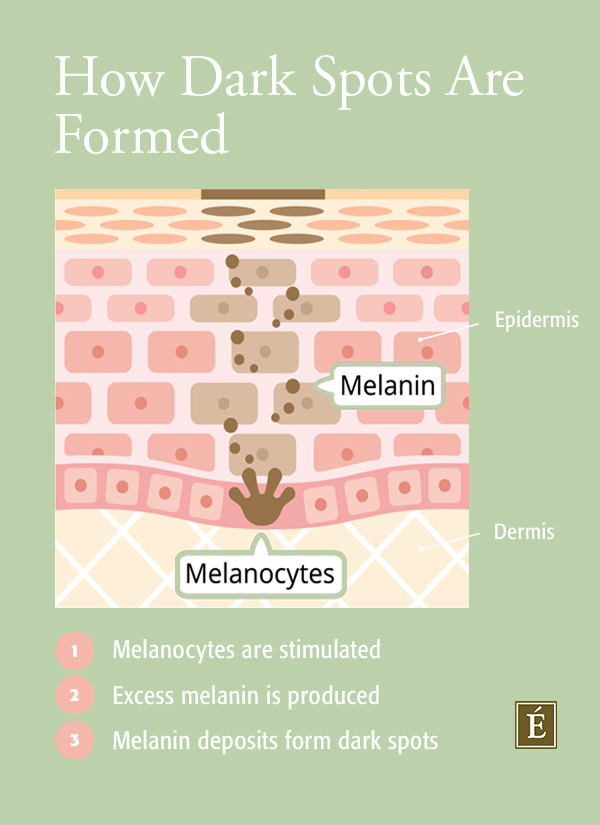
What Causes Dark Spots?
Whether your skin tone is dark or light, your skin contains a pigment called melanin. Produced by cells called melanocytes, melanin acts as a form of protection for the skin. However, when hyperpigmentation occurs, your skin produces excess melanin which forms deposits, creating spots and patches darker in color than the surrounding skin. Although hyperpigmentation affects people of all skin colors, it tends to affect darker skin types more frequently. Here are three reasons why you could be suffering from dark spots:
Sun Exposure
The number one cause of dark spots is sun damage. When stimulated by harmful UV rays, melanocytes react by releasing melanin which acts as a natural sunscreen. Melanin is useful because it absorbs the energy from UV rays and redistributes it. However, the sun can trigger the production of too much melanin, causing dark spots and patches of skin.
The sun is not just the root problem for sun spots, it also causes the dark marks that we call age spots or liver spots. This type of hyperpigmentation is also caused by sun damage, accumulated over many years of exposure.“As you age,” according to Harvard Health Publishing, “years of being in the sun start to add up.” Most common in adults over the age of 55, these tan, brown or black spots tend to speckle the areas most exposed to the sun: face, hands, back, feet and shoulders. Aging can also intensify the appearance of hyperpigmentation for two reasons. First, as we age, melanocytes decrease in number but increase in size and pigment production. Second, older skin tends to look thinner, paler and more translucent, emphasizing the appearance of dark spots.
Hormones
When hormone levels zigzag up and down, one of the most common side effects is a change in pigmentation called melasma. Frequently seen during pregnancy, hormonal therapies or even changes in birth control, a rise in hormones stimulates the production of melanin. Pregnant women often develop dark patches on the nose, cheeks, jawline, forehead or chin, creating a pattern called “mask of pregnancy” or “chloasma.” This type of hyperpigmentation typically lasts until pregnancy ends or hormonal levels return to balance.
Exposure to the sun and heat can worsen the appearance of this hormonally-triggered hyperpigmentation. If you suffer from melasma and hope to unwind in a sauna or a session of hot yoga, you may want to rethink your chillaxing plans. A high-temperature environment can affect your hyperpigmentation and dark spots, helping dark patches enlarge and spread.
Inflammation
Dark spots can sometimes develop after inflammation or an injury to the skin, especially for those suffering from acne, eczema, allergic reactions or other skin conditions. Termed post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, this type of discoloration is the skin’s natural response to inflammation. After a wound occurs, the skin becomes inflamed and, as it heals, the skin naturally produces excess melanin which darkens the skin.
Hyperpigmentation due to inflammation is especially common after breakouts. As the irritated skin heals from acne, a dark spot is left behind, ranging in color from pink to red, purple, brown or black. The worse the inflammation, the larger and darker the spot can be. Also, there’s a reason why the experts warn you to avoid picking your acne. Popping those pimples can increase the likelihood of developing pimple inflammation or a dark spot.

How To Prevent Dark Spots (Hyperpigmentation)
Protecting your skin from further damage is just as important as reducing existing hyperpigmentation. These are our top tips for preventing further dark spots from appearing on the skin:
Shield Yourself From the Sun
Brian Goodwin, International Educator at Eminence Organic Skin Care, says that time in the sun plays a "significant role" in the development of hyperpigmentation. It’s easy to underestimate its true impact. "Since we typically see the results of a day in the sun after we’ve retreated indoors, you may not realize that your consistent sun care habits (or lack thereof) are responsible for the formation of hyperpigmentation," he says.
Since sun damage is one of the top causes of dark spots — including age spots — preventing exposure to UV rays is essential to preventing hyperpigmentation. This means staying out of the sun, wearing a hat outdoors and slathering on sunscreen. By avoiding or blocking UV rays that stimulate the production of melanin, dodging the sun is one of the best ways to prevent dark spots.
Product Picks
Avoid Heat
UV rays are not the only triggers for melanin production. Sources of heat can also stimulate melanocytes to produce more pigment. Avoid activity with major heat exposure and keep the skin cool to reduce this potential problem for dark spots.
Stop Inflammation
Because inflammation is another major reason for hyperpigmentation, you’ll want to stop any harmful habits that injure or inflame the skin. Pimple picking is a no-no, as are any other activities that aggravate your complexion.
Use Vitamin C Regularly
Experts advise that a topical antioxidant like a Vitamin C serum helps with the look of dark spots when applied on a regular basis. Because Vitamin C interferes with melanin production (and provides so many other benefits for the skin!), keeping a bottle of this antioxidant-rich skin care product on hand is another essential step for preventing hyperpigmentation.
With this guide on the whys and hows of hyperpigmentation, we’re confident that you can even your skin tone and treat any pesky spots. Do you suffer from dark spots? Visit your nearest Eminence Organics Spa Partner to get a personalized skin care consultation.





